Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Preparation Instructions
What Is Flexible Sigmoidoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a procedure used to see inside the sigmoid colon and rectum. Flexible sigmoidoscopy can detect inflamed tissue, abnormal growths, and ulcers. The procedure is used to look for early signs of cancer and can help doctors diagnose unexplained changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain, bleeding from the anus, and weight loss.
What Are The Sigmoid Colon And Rectum?
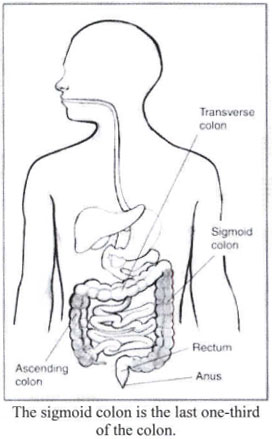
The sigmoid colon is the last one-third of the colon. The colon comprises three main parts: the ascending colon, the transverse colon. and the sigmoid colon-sometimes called the descending colon. The colon absorbs nutrients and water and forms stool.
The rectum is about 6 inches long and connects the sigmoid colon to the anus. StooJ leaves the body through the anus. Muscles and nerves in the rectum and anus control bowel movements.
How Is Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Different From Colonoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy enables the doctor to see only the sigmoid colon, whereas colonoscopy allows the doctor to see the entire colon. Colonoscopy is the preferred screening method for cancers of the colon and rectum; however, to prepare for and perform a f1exible sigmoidoscopy usually requires less time.
How Is A Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Performed?
Examination of the Sigmoid Colon
During a flexible sigmoidoscopy, patients lie on their left side on an examination table. The doctor inserts a long, flexible, lighted tube called a sigmoidoscope, or scope, into the anus and slowly guides it through the rectum and into the sigmoid colon. The scope inflates the colon with air to give the doctor a better view. A small camera mounted on the scope transmits a video image from inside the colon to a computer screen, allowing the doctor to carefully examine the tissues lining the sigmoid colon and rectum. The doctor may ask the patient to move periodically so the scope can be adjusted for better viewing.
When the scope reaches the transverse colon, the scope is slowly withdrawn while the lining of the colon is carefully examined again.
Recovery
A flexible sigmoidoscopy takes about 20 minutes. Cramping or bloating may occur during the fi rst hour after the procedure. Bleeding and puncture of the large intestine are possible but uncommon complications. Discharge instructions should be carefully read and followed.
Patients who develop any of these rare side effects should contact their doctor immediately:
- severe abdominal pain
- fever
- bloody bowel movements
- dizziness
- weakness
